Benefits
What is dyslexia?
Dyslexia is a learning disorder that affects the way individuals process and understand written language. It is characterized by difficulties in reading, spelling, and writing, despite having normal intelligence and adequate educational opportunities.
Dyslexia symptoms
There are various symptoms that may indicate the presence of dyslexia. Dyslexia is a learning disorder that affects the brain's ability to process written language. It is characterized by difficulties in reading, writing, and spelling. While dyslexia is a lifelong condition, with the right support and strategies, individuals with dyslexia can succeed in school and beyond.
Some common signs of dyslexia include:
Difficulty in reading fluently and accurately: People with dyslexia may struggle to read at the same pace as their peers. They may have difficulty recognizing and decoding words, leading to slow and laborious reading.
Struggling with spelling, including frequently misspelling words: Dyslexia can affect a person's ability to understand the relationship between sounds and letters, making spelling a challenge. Individuals with dyslexia may frequently misspell words or have difficulty remembering the correct spelling.
Challenges in writing, such as poor handwriting or problems organizing thoughts on paper: Dyslexia can impact a person's ability to express their thoughts in writing. They may have difficulty organizing their ideas, structuring sentences, or maintaining coherence in their writing. Additionally, dyslexia can also affect handwriting, resulting in messy or illegible writing.
Trouble remembering or comprehending what has been read: Dyslexia can affect a person's working memory, making it difficult to retain and comprehend information from written texts. Individuals with dyslexia may struggle to understand the main ideas, make inferences, or remember details from what they have read.
Difficulties with sequencing or processing information in the correct order: Dyslexia can impact a person's ability to process and organize information in a sequential manner. They may have trouble following instructions, understanding the order of events, or organizing their thoughts in a logical sequence.
It's important to note that dyslexia symptoms can vary from person to person, and not all individuals experience every symptom. Some individuals may exhibit more pronounced difficulties in reading, while others may struggle primarily with spelling or writing. The severity of dyslexia symptoms can also vary, with some individuals experiencing mild challenges and others facing more significant obstacles.
Early identification and intervention are crucial in supporting individuals with dyslexia. With appropriate accommodations, such as specialized instruction, assistive technology, and supportive learning environments, individuals with dyslexia can develop effective strategies to overcome their challenges and reach their full potential.
Dyslexia in children
Dyslexia often becomes apparent during childhood, typically when children start learning to read and write. It is a learning disorder that affects the ability to process language, making it difficult for individuals to read, write, and spell accurately.
Children with dyslexia may struggle with letter recognition, phonological awareness, and decoding words. They might find it challenging to read aloud, understand written instructions, or remember sight words. These difficulties can lead to frustration and a lack of confidence in their academic abilities.
It is important to note that dyslexia is not a reflection of a child's intelligence or effort. In fact, many individuals with dyslexia are highly intelligent and possess unique strengths in areas such as problem-solving, creativity, and critical thinking.
When a child is diagnosed with dyslexia, early intervention is crucial. With proper support and interventions, children with dyslexia can develop strategies to overcome their challenges and succeed in school. One common intervention is the use of multisensory teaching methods, which engage multiple senses to reinforce learning. For example, a teacher may incorporate visual aids, auditory cues, and tactile activities to help a child with dyslexia grasp and retain information.
Another effective strategy is the implementation of assistive technology. There are various tools and software available that can assist individuals with dyslexia in reading and writing. Text-to-speech software, for instance, can read aloud written text, making it easier for children with dyslexia to comprehend and follow along.
Furthermore, it is essential for parents, teachers, and other educational professionals to create a supportive and inclusive environment for children with dyslexia. This includes providing additional time for assignments and tests, offering alternative methods of assessment, and fostering a positive mindset towards learning.
It is important to recognize and celebrate the unique strengths and talents of children with dyslexia. Many individuals with dyslexia excel in areas such as art, music, sports, and entrepreneurship. By nurturing these talents and providing opportunities for success, we can empower children with dyslexia to reach their full potential.
In conclusion, dyslexia is a learning disorder that affects children's ability to read, write, and spell accurately. However, with early intervention, appropriate support, and a nurturing environment, children with dyslexia can overcome their challenges and thrive academically and personally.
Dyslexia in adults
Dyslexia is not limited to childhood, as individuals with dyslexia continue to experience these challenges into adulthood. Adults with dyslexia often have difficulty with tasks that involve reading and writing, such as filling out forms, reading instructions, or following written directions.
Moreover, dyslexia can have a significant impact on various aspects of an adult's life, including their personal relationships, social interactions, and self-esteem. The challenges faced by adults with dyslexia can extend beyond the realm of academics and professional life, affecting their day-to-day activities and overall well-being.
For instance, individuals with dyslexia may struggle with reading books, newspapers, or even simple labels on grocery items. This can make it difficult for them to access information, stay informed about current events, or simply enjoy the pleasure of reading for leisure.
In addition, dyslexia can pose challenges in the workplace. Adults with dyslexia may find it challenging to keep up with written communication, such as emails, memos, or reports. They may require additional time and effort to comprehend written information, which can lead to feelings of frustration and stress.
Furthermore, dyslexia can affect an individual's professional life, making certain careers or job responsibilities more challenging. For example, professions that heavily rely on written communication, such as journalism, law, or academia, may present unique difficulties for adults with dyslexia. However, it's important to remember that dyslexia does not determine someone's intelligence or abilities, and many adults with dyslexia have successful careers in various fields.
Despite the challenges they face, adults with dyslexia often develop coping strategies and utilize assistive technologies to overcome obstacles in their daily lives. These may include using text-to-speech software, employing organizational tools, or seeking support from dyslexia specialists or support groups.
It is crucial for society to recognize and accommodate the needs of adults with dyslexia. By fostering an inclusive environment that provides appropriate support and resources, we can empower individuals with dyslexia to reach their full potential and thrive in all aspects of their lives.
How to diagnose dyslexia
Diagnosing dyslexia involves a comprehensive assessment conducted by qualified professionals, such as educational psychologists or specialists in learning disabilities. The diagnostic process typically includes:
Gathering information about the individual's developmental history and academic performance
During the diagnostic process, professionals gather detailed information about the individual's developmental history and academic performance. This includes reviewing past school records, conducting interviews with teachers and parents, and analyzing previous assessments. By examining these factors, professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the individual's educational journey and identify any potential areas of concern.
Administering standardized tests and assessments to evaluate reading, writing, and language skills
To assess an individual's reading, writing, and language skills, professionals administer a series of standardized tests and assessments. These tests are specifically designed to measure various aspects of literacy and language processing. They may include tasks such as reading comprehension exercises, spelling tests, and language proficiency assessments. By evaluating performance on these tests, professionals can identify specific areas of difficulty and determine if dyslexia is present.
Conducting interviews with the individual and their parents or caregivers to understand their experiences and challenges
During the diagnostic process, professionals conduct interviews with both the individual and their parents or caregivers. These interviews provide an opportunity to gain insight into the individual's experiences and challenges related to reading and learning. By listening to their perspectives, professionals can gather valuable information about the impact of dyslexia on the individual's daily life and educational journey. This collaborative approach ensures that the diagnostic process takes into account the unique experiences and needs of the individual.
Considering additional factors that may impact reading and learning abilities, such as hearing or vision impairments
In addition to assessing reading and language skills, professionals also consider other factors that may impact an individual's reading and learning abilities. This includes evaluating hearing and vision capabilities to rule out any impairments that may contribute to difficulties in reading and processing written information. By considering these additional factors, professionals can ensure that the diagnosis is accurate and comprehensive.
It is essential to obtain a formal dyslexia diagnosis to access appropriate support and accommodations in educational settings. Once a diagnosis is established, individuals with dyslexia can receive targeted interventions and accommodations to help them succeed academically and reach their full potential.
Text to speech and other tools for dyslexia
Various assistive technologies and tools can assist individuals with dyslexia in improving their reading and writing skills. One such tool is text-to-speech software, which reads written text aloud, helping individuals better comprehend the content. A good example is Speak4Me, an app that allows users to turn any written text into audio.
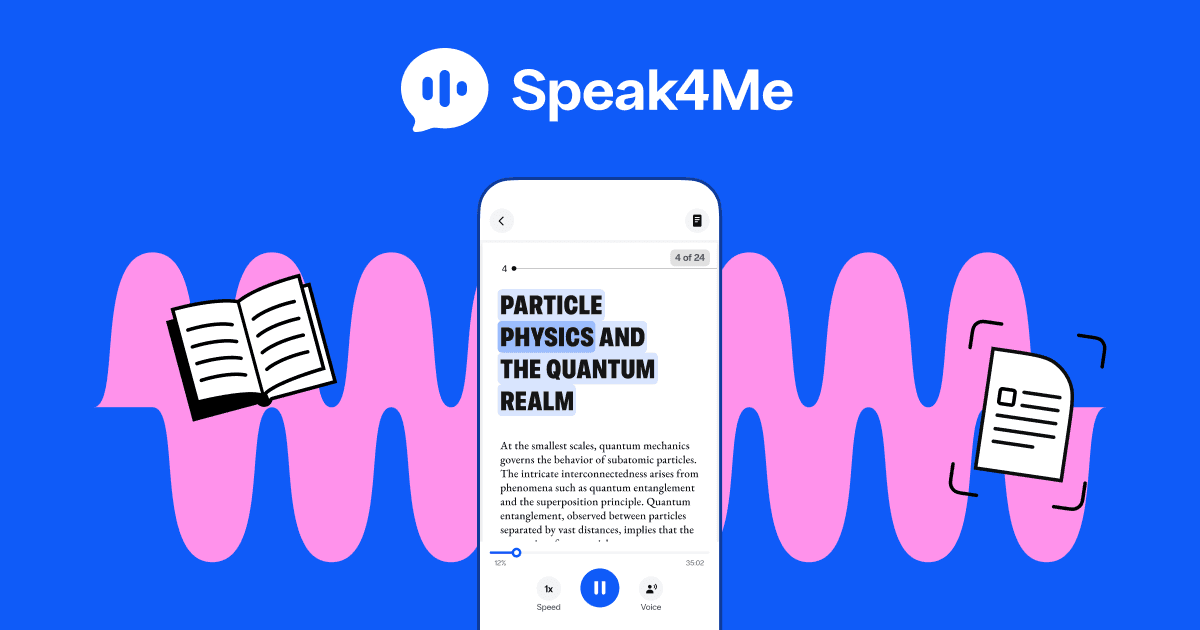
Other helpful tools include:
Speech recognition software, which transcribes spoken words into written text, easing the writing process
Word prediction software, which suggests words as individuals type, aiding spelling and vocabulary
Reading apps and e-books with customizable fonts, colors, and layouts that enhance readability
These tools can provide valuable support to individuals with dyslexia, promoting increased independence and confidence in their daily lives.
In conclusion, dyslexia is a learning disorder characterized by difficulties in reading, writing, and spelling. It can affect individuals of all ages, with symptoms varying from person to person. Early intervention and appropriate support are crucial in helping individuals with dyslexia overcome their challenges and reach their full potential.
Try Speak4Me for free and overcome dyslexia!

